What is body mass index, or BMI?
Body mass index (BMI) body mass index (or BMI) is an indicator expressing the ratio of a person's weight to height, which is used to determine underweight, normal weight, and overweight. It was developed by Adolphe Quetelet in the 19th century.. Quetelet wanted to find a universal method that would allow people to quantify and compare their weight distribution. His work led to the creation of the Quetelet index, which is now known as the body mass index. Initially, it was not intended to assess a person's obesity, but rather to describe the average person's body composition. In the 1970s, scientists noticed a connection between BMI and the problems associated with obesity and overweight, and today BMI is one of the most common methods for assessing body composition and health.
Calculating body mass index or BMI
Normal values for body mass index at different ages
Underweight, normal weight and overweight in adults
Underweight, normal weight and overweight in children and adolescents
The importance of calculating body mass index
How to achieve ideal weight and a healthy body mass index?
 Although the relationship between body mass index and body fat content is quite strong, there are certain differences. Body mass index does not take into account:
Although the relationship between body mass index and body fat content is quite strong, there are certain differences. Body mass index does not take into account:
- more accurate body composition, i.e. the amount of fat and muscle mass, or the distribution of fat in the body;
- individual differences, such as bone structure, muscle mass, or body shape;
- age and gender differences, for example, age can be accompanied by a natural decrease in muscle mass and accumulation of fat.
For example, with the same body mass index,
- women usually have more body fat than men;
- Older adults typically have a higher percentage of body fat than younger adults;
- differences in body fat content in different ethnic groups;
- Pregnant women experience physiological changes and their body mass composition is different from normal;
- Athletes often have less body fat than non-athletes.
In addition, the method of calculating body mass index (BMI) is not suitable for certain medical conditions.
Therefore, it is recommended to use the BMI formula for individual assessment. One way to do this is to also consider waist and hip circumference in addition to BMI.
Calculating body mass index or BMI
You can also find them on the Internet. body mass index calculators, where you can enter your weight, height and sometimes also your age and gender. The weight calculator on the Health Insurance Fund website also gives you an idea of where your weight stands compared to other Estonians, Europeans and Americans, where you stand compared to your peers of the same age and gender, and how you can improve your health.
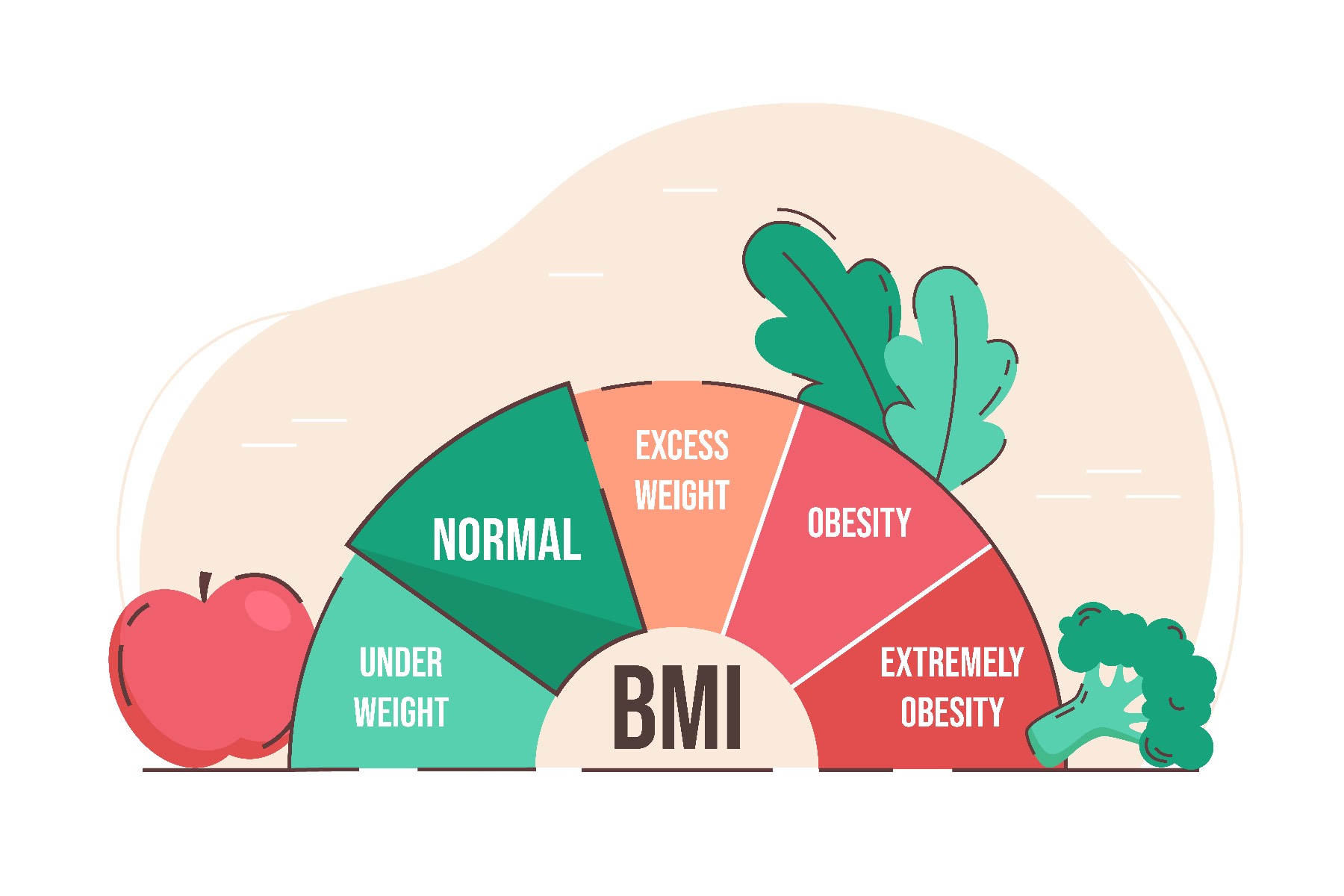
Standard weight categories are used when interpreting BMI for adults aged 20 and over, so the normal values for BMI are the same for women and men. For children and young people, BMI is age-dependent, as body fat content varies by age.
BMI calculators like these can help you find out what your body mass index is based on current data. They are cheap and easy tools for determining overweight and obesity. Other methods of measuring body fat Examples include skinfold thickness measurement, underwater weighing, bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). These methods are not always readily available – they are often either expensive or require highly trained personnel to perform.
Body mass index formula
The formula for body mass index is as follows: weight (kg) / height (m²). For example, if a person weighs 70 kg and is 160 cm tall, then according to the BMI formula, their body mass index is 27.3 (70 / 1.6 x 1.6 = 27.3). According to the normal values in the body mass index table, such a BMI indicates obesity.
Normal values for body mass index at different ages
The values indicating underweight, normal weight, and overweight are different for adults, children, young people, and the elderly. The body mass index method is intended primarily for adults aged 20-65.
Underweight, normal weight and overweight in adults
The normal range for adults is 18.5-24.9. A BMI below 18.5 indicates underweight. According to the WHO classification, BMIs between 25.0-29.9 indicate overweight, and values greater than 30.0 indicate obesity.
Underweight, normal weight and overweight in the elderly
Physiological changes associated with aging cause a decrease in body height and weight. For the elderly, a body mass index between 23 and 29.9 is considered normal, but a body mass index between 25 and 27 is considered optimal. For those over 65, being underweight (below BMI 23) can be more dangerous and increase the risk of mortality than being slightly overweight. Eating too little and being underweight can lead to feelings of weakness, increase the risk of falling, and may reduce independent functioning and quality of life. Being underweight can weaken the immune system, muscle and lung function, and slow down wound healing. and bone healing.
Underweight, normal weight and overweight in children and adolescents
In Estonia, weight-growth charts prepared by pediatricians are used to assess overweight in children aged 2–18. Body mass index indicators are also monitored in children and young people, but this depends on age and the BMI norm is different from adults. Over the years, the weight problem has grown and 301% of primary school students are overweight.
Several studies have been conducted in Estonia on the weight of children and young people and related topics. Here are some examples of studies conducted in Estonia:
- Estonian School Student Health Behavior Survey (HBSC Survey): This is an international survey of health behaviours among schoolchildren, conducted every four years. The survey collects data on health behaviours, including weight, diet, physical activity and health status, among 11-, 13- and 15-year-old students.
- Estonian Student Growth Survey (COSI): This is a European study (WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative or COSI) that collects anthropometric data on childhood obesity at three-year intervals. The study is conducted among 6-9 year-olds.
Why might calculating body mass index be important?
Although such body mass indices can be useful indicators for assessing underweight or obesity and the potential health risks associated with them, it is not possible to assess the state of health comprehensively by calculating BMI alone. If health risks are suspected, it is possible and necessary to conduct additional examinations. Thus, a person of normal weight can also have health problems, and at the same time, an overweight or underweight person can be healthy. Below, we present some reasons why it may be useful to calculate BMI using a weight calculator based on your current weight and height.
A body mass significantly different from normal weight is a health risk. The risk of certain diseases increases significantly when a person's BMI exceeds 27. If the BMI is over 30, it is considered obesity and it seriously impairs health.
A high body mass index (BMI) can pose several health risks. Overweight and obesity are associated with several health risks and comorbidities, including:
- Type 2 diabetes,
- insulin resistance,
- dyslipidemia,
- metabolic syndrome,
- cardiovascular diseases,
- respiratory diseases (including asthma, sleep apnea),
- osteoarthritis,
- some malignant tumors (e.g. digestive system tumors, endometrial, cervical or ovarian cancer in women, breast cancer after menopause, prostate cancer in men),
- digestive system diseases (gallbladder, pancreas, gastroesophageal reflux),
- urinary and genital tract disorders (chronic kidney disease, kidney stones, stress incontinence, infertility problems, menstrual cycle disorders in women),
- psychological and social risks.
There are several factors that contribute to overweight and high body mass index., for example:
- lifestyle, including exercise and eating habits;
- social relationships, such as the influence of loved ones;
- psychological factors, such as stress and mental health conditions;
- socioeconomic status, such as education, income;
- biological factors, such as genetics, hormone function, microbiota;
- environmental factors, such as politics and food availability;
- sociodemographic factors, such as gender, age, ethnicity.
Therefore, an individual approach and a holistic view of a person's life are necessary to understand what changes need to be implemented to achieve a normal weight. If you are concerned about your health, it would be advisable to consult a healthcare professional for more detailed information and advice, if necessary.
How to achieve ideal weight and a healthy body mass index?
Estonian adult population health behavior survey According to data (2022), the body mass index (BMI) of the working-age population in Estonia has been increasing consistently over the past 20 years. According to the study, 38.71% of men and 26.71% of women were overweight, and 22.31% of men and 20.11% of women were obese.
In the case of obesity, the most important action in terms of reducing body weight and health risks is to change your lifestyle. A healthy lifestyle includes, among other things, sufficient exercise and a nutritious diet. It is important to be persistent and consistent in reducing body weight through diet and exercise habits.
The Estonian Institute for Health Development has compiled an exercise pyramid, which outlines the main recommendations to follow when developing physical activity habits. It is important to reduce sedentary activities, be as mobile as possible, and find enough time for aerobic activities and stretching, balance, and strength exercises.
In addition to an active lifestyle, it is important to pay attention to your eating habits. General dietary recommendations are given below. In the food pyramid created by the Estonian Institute for Health Development. It has also been created sugar calculator, which allows us to find out how much sugar we actually consume. In addition to the body mass index calculator, the Nutridata website also energy recommendation calculatorIn addition to calculators, Nutridata's free nutrition program allows you to keep a food and exercise diary, analyze eating habits, and test sample menus.
The Estonian Institute for Health Development has prepared several publications:
- General nutrition and exercise recommendations
- Eating and exercise recommendations for the elderly
- Nutrition and food recommendations for young people
- Dietary recommendations for children and young people
- Nutrition and food recommendations for pregnant and breastfeeding mothers
There are various options for nutrition. Read recommendations on our blog toot. In addition, we carry out lifestyle trainingto help people achieve a fulfilling and healthier lifestyle and achieve their ideal weight. In lifestyle training, we approach a person's life holistically, addressing different areas of life. The topics of this 6-part training are as follows:
- CHOICES. We all have choices, sometimes we just don't see them.
- NUTRITION. There are many different eating styles, and everyone can analyze which one is right for them.
- ENVIRONMENT: Unfortunately, healthy eating is not possible without changing your environment and some planning.
- REST. The quality of our sleep has a significant impact on our weight. There is also talk of intermittent fasting.
- RELATIONSHIPS, ATTITUDES, TRUST. It is difficult to overestimate the importance of relationships and attitudes to weight and health.
- ACTIVITY: Physical activity as part of a healthy lifestyle and its role in weight loss.

Vallo Põldaru
TrainerVallo is a marketer by profession, a specialist in human internet behavior, and a trainer whose favorite topics are marketing psychology, spiritual care, and sustainable mental health in today's society.
Estonians eat too little fiber





